In a new blog post, Facebook VP of Product Partnerships Ime Archibong addressed the company’s latest user privacy controversy. The rebuttal is the second round of Facebook’s push back against Tuesday’s report by the New York Times detailing some of Facebook’s special partnerships and extensive data sharing with major tech players.
In the new post, Archibong specifically argues that Facebook never allowed its partners to access private Facebook messages without a user’s permission. While Facebook did in fact share user messages with third parties, the company claims it only did so “if they chose to use Facebook Login.” Facebook Login allows users to log into third party sites without making a specific new set of login credentials.
As Archibong writes:
“We worked closely with four partners to integrate messaging capabilities into their products so people could message their Facebook friends — but only if they chose to use Facebook Login. These experiences are common in our industry — think of being able to have Alexa read your email aloud or to read your email on Apple’s Mail app.”
He goes on to claim that these features “were experimental and have now been shut down for nearly three years.” Facebook is being purposefully quite specific here about what this particular timeline applies to, as the New York Times story reports that the company engaged in some forms of “special access” data sharing with third parties “as recently as this summer, despite public statements that it had stopped that type of sharing years earlier.”
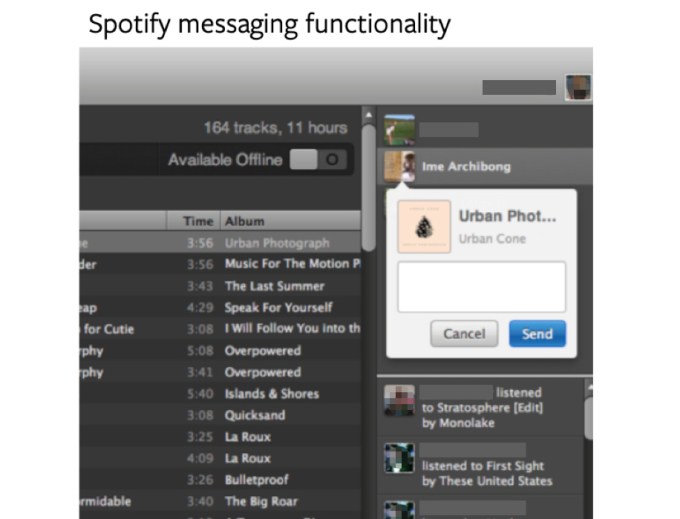
As to the question of why Facebook would grant messaging partners deep messaging access:
“That was the point of this feature — for the messaging partners mentioned above, we worked with them to build messaging integrations into their apps so people could send messages to their Facebook friends…
In order for you to write a message to a Facebook friend from within Spotify, for instance, we needed to give Spotify “write access.” For you to be able to read messages back, we needed Spotify to have “read access.” “Delete access” meant that if you deleted a message from within Spotify, it would also delete from Facebook. No third party was reading your private messages, or writing messages to your friends without your permission.”
Facebook’s post provides screenshots of these messaging integrations, which happened long enough ago that most of us don’t remember them at all. What Facebook declined to provide in this post: the permissions screens that users saw when granting this access. Those will be key in determining just how informed users were of what they were handing over when casually enabling these integrations.
screenshot via Facebook
Still, no matter how clearly Facebook might have worded the permissions screens, social media users are only just now broadly awakening to the fact that something is unsettling about all of this data sharing. The fact remains that even if users clicked to grant their consent for a feature like this, it’s a problem that they didn’t understand the privacy implications of doing so.
In this instance, it isn’t just Facebook’s problem. With privacy regulation looming on the horizon in the U.S. and the GDPR already making major waves for consumer privacy in the EU, it’s only a matter of time before all major tech companies that rent user data to advertisers face a reckoning that could change everything about the way they do business.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2rO7Ukd
via IFTTT
Comments
Post a Comment