Tell someone not to do something and sometimes they just want to do it more. That’s what happened when Facebook put red flags on debunked fake news. Users who wanted to believe the false stories had their fevers ignited and they actually shared the hoaxes more. That led Facebook to ditch the incendiary red flags in favor of showing Related Articles with more level-headed perspectives from trusted news sources.
But now it’s got two more tactics to reduce the spread of misinformation, which Facebook detailed at its Fighting Abuse @Scale event in San Francisco. Facebook’s director of News Feed integrity Michael McNally and data scientist Lauren Bose held a talk discussing all the ways it intervenes. The company is trying to walk a fine line between censorship and sensibility.
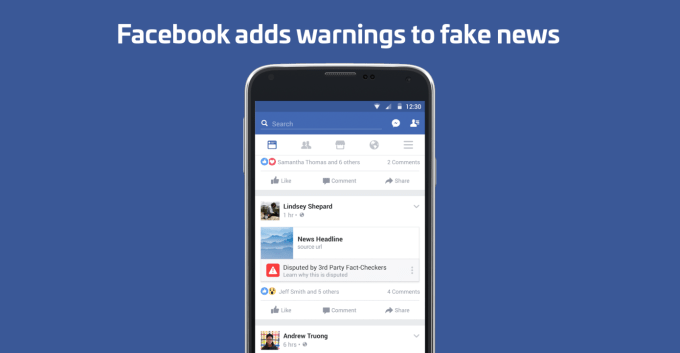
These red warning labels actually backfired and made some users more likely to share, so Facebook switched to showing Related Articles
First, rather than call more attention to fake news, Facebook wants to make it easier to miss these stories while scrolling. When Facebook’s third-party fact-checkers verify an article is inaccurate, Facebook will shrink the size of the link post in the News Feed. “We reduce the visual prominence of feed stories that are fact-checked false,” a Facebook spokesperson confirmed to me.
As you can see below in the image on the left, confirmed-to-be-false news stories on mobile show up with their headline and image rolled into a single smaller row of space. Below, a Related Articles box shows “Fact-Checker”-labeled stories debunking the original link. Meanwhile on the right, a real news article’s image appears about 10 times larger, and its headline gets its own space.

Second, Facebook is now using machine learning to look at newly published articles and scan them for signs of falsehood. Combined with other signals like user reports, Facebook can use high falsehood prediction scores from the machine learning systems to prioritize articles in its queue for fact-checkers. That way, the fact-checkers can spend their time reviewing articles that are already qualified to probably be wrong.
“We use machine learning to help predict things that might be more likely to be false news, to help prioritize material we send to fact-checkers (given the large volume of potential material),” a spokesperson from Facebook confirmed. The social network now works with 20 fact-checkers in several countries around the world, but it’s still trying to find more to partner with. In the meantime, the machine learning will ensure their time is used efficiently.
Bose and McNally also walked the audience through Facebook’s “ecosystem” approach that fights fake news at every step of its development:
- Account Creation – If accounts are created using fake identities or networks of bad actors, they’re removed.
- Asset Creation – Facebook looks for similarities to shut down clusters of fraudulently created Pages and inhibit the domains they’re connected to.
- Ad Policies – Malicious Pages and domains that exhibit signatures of wrong use lose the ability to buy or host ads, which deters them from growing their audience or monetizing it.
- False Content Creation – Facebook applies machine learning to text and images to find patterns that indicate risk.
- Distribution – To limit the spread of false news, Facebook works with fact-checkers. If they debunk an article, its size shrinks, Related Articles are appended and Facebook downranks the stories in News Feed.
Together, by chipping away at each phase, Facebook says it can reduce the spread of a false news story by 80 percent. Facebook needs to prove it has a handle on false news before more big elections in the U.S. and around the world arrive. There’s a lot of work to do, but Facebook has committed to hiring enough engineers and content moderators to attack the problem. And with conferences like Fighting Abuse @Scale, it can share its best practices with other tech companies so Silicon Valley can put up a united front against election interference.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2r6F3Hl
via IFTTT
Comments
Post a Comment