Anyone can access portions of a web portal, used by law enforcement to request customer data from Amazon, even though the portal is supposed to require a verified email address and password.
Amazon’s law enforcement request portal allows police and federal agents to submit formal requests for customer data along with a legal order, like a subpoena, a search warrant, or a court order. The portal is publicly accessible from the internet, but law enforcement must register an account with the site in order to allow Amazon to “authenticate” the requesting officer’s credentials before they can make requests.
Only time sensitive emergency requests can be submitted without an account, but this requires the user to “declare and acknowledge” that they are an authorized law enforcement officer before they can submit a request.
The portal does not display customer data or allow access to existing law enforcement requests. But parts of the website still load without needing to log in, including its dashboard and the “standard” request form used by law enforcement to request customer data.
The portal provides a rare glimpse into how Amazon handles law enforcement requests.
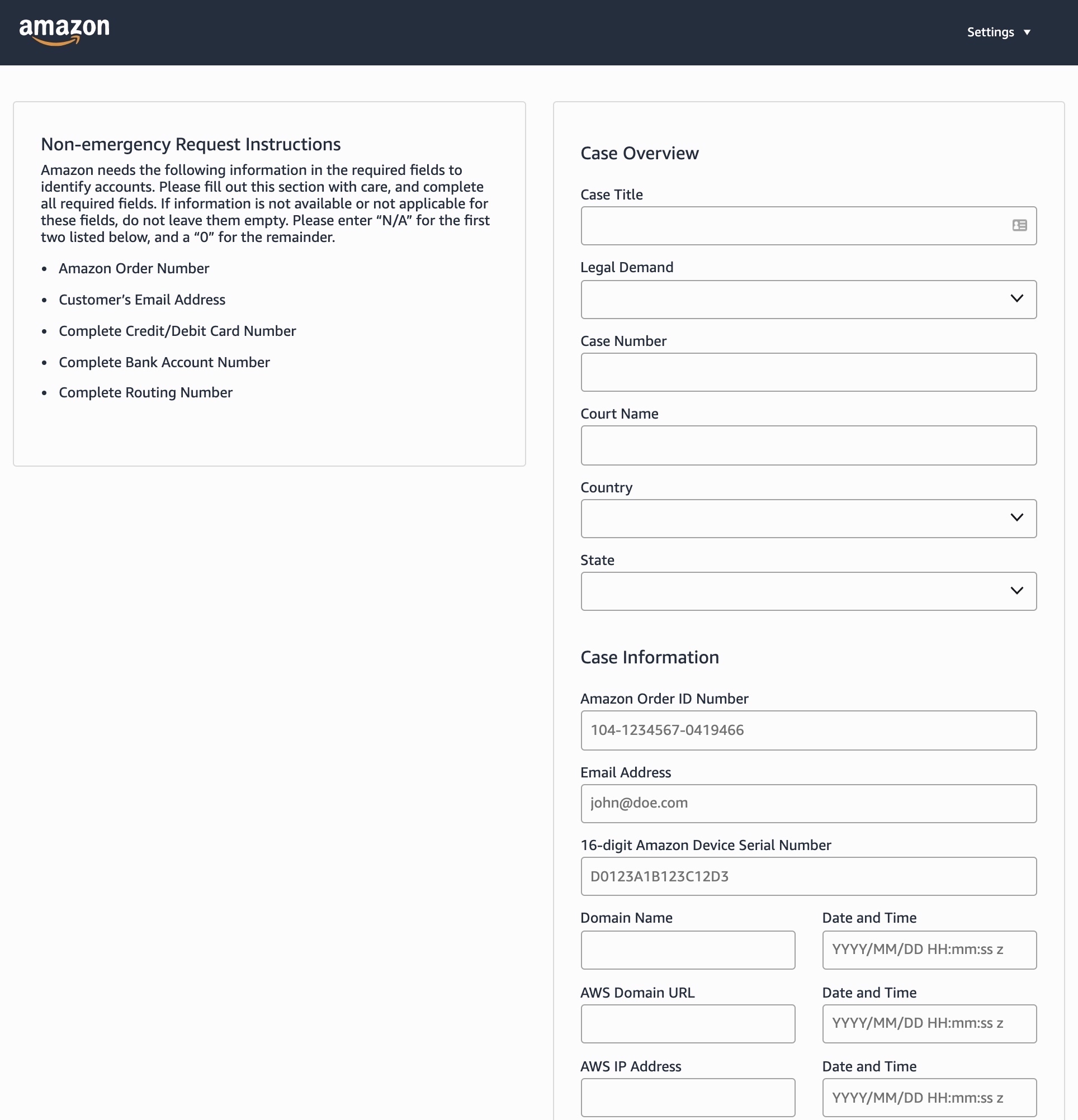
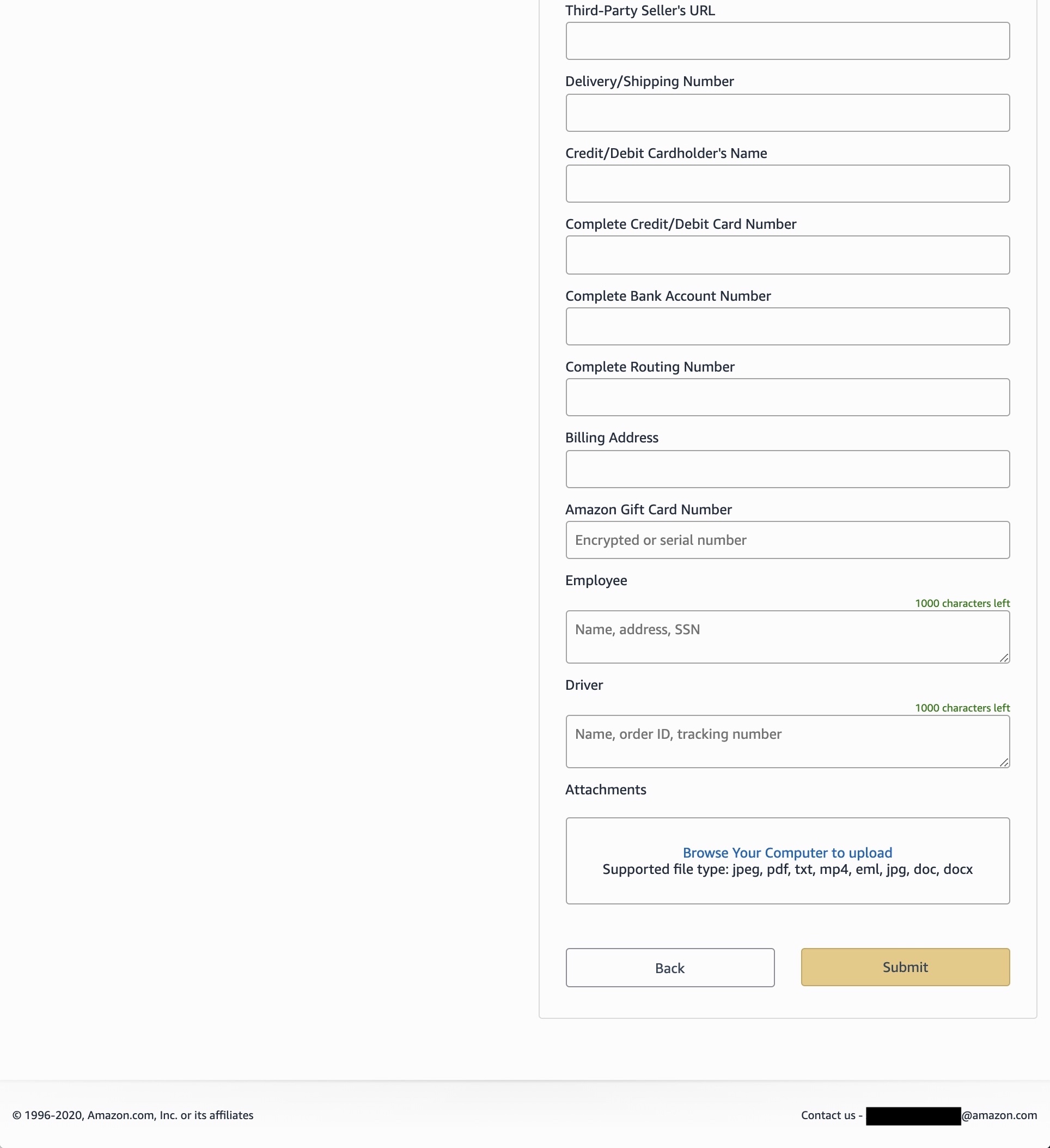
This form allows law enforcement to request customer data using a wide variety of data points, including Amazon order numbers, serial numbers of Amazon Echo and Fire devices, credit cards details and bank account numbers, gift cards, delivery and shipping numbers, and even the Social Security number of delivery drivers.
It also allows law enforcement to obtain records related to Amazon Web Services accounts by submitting domain names or IP addresses related to the request.
Assuming this was a bug, we sent Amazon several emails prior to publication but did not hear back.
Amazon is not the only tech company with a portal for law enforcement requests. Many of the bigger tech companies with millions or even billions of users around the world, like Google and Twitter, have built portals to allow law enforcement to request customer and user data.
Motherboard reported a similar issue earlier this month that allowed anyone with an email address to access law enforcement portals set up by Facebook and WhatsApp.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/3mT4ic5
via IFTTT
Comments
Post a Comment