Here’s a horror scenario for you: you’re flying in a small plane and suddenly the single pilot who knows how to fly passes out. In the movies, somebody would probably talk one of the passengers through safely landing the plane. In reality, that’s unlikely. Flying planes is hard.
Now, however, planes outfitted with the Garmin G3000 flight deck, will have the option to include a system that will land the plane in an emergency with just the push of a button.
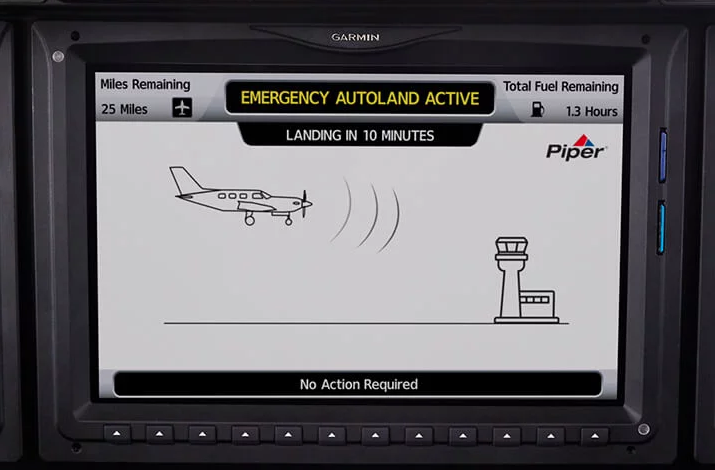
Autoland combines all of the navigation and communications tech in the plane and combines that with a sophisticated autopilot. Once a passenger activates the autoland feature — or the plane determines that the pilot is incapacitated — the system will look at all the available information about weather, remaining fuel on board and the local terrain to plot a route to the nearest suitable airport. It’ll even alert air traffic control about what’s happening, so they can route other planes around you.
The system also then takes over all of the touchscreens in the plane that are part of the G3000 flight deck and displays a simplified interface that allows the passengers to talk to air traffic control — and very little else.
Taking all of that information into account, the plane then plans the decent, lands the plane and shuts down the engines.
“The vision and development of the world’s first Autoland system for general aviation was a natural progression for Garmin as we looked at our aircraft systems and existing autonomous technologies and recognized it is our responsibility to use these building blocks to deliver a technology that will change lives and revolutionize air travel,” said Phil Straub, Garmin executive vice president and managing director of aviation.
It’s important to note that this is meant to be a system that’s only activated in the case of an emergency. Since it automatically alerts the authorities when somebody presses the button, nobody is going to activate it unless it’s absolutely necessary — and the FAA would surely want to ask you a few questions.
It does show, however, that we’re getting closer to a time where autopilot systems get significantly smarter. The number of variables a system like Autoland has to deal with is relatively small compared to those an autonomous car in a city has to navigate, after all. And autopilot systems for planes have already become quite sophisticated.
The launch partners for Autoland are Piper and Cirrus, who are making it an option in the 2020 models of the Piper M600 turboprop and Cirrus Vision Jet, pending FAA authorization. Those cost a few million dollars, though, so you better save up. Existing planes with the Garmin G3000 cockpit may also be retrofitted with the autoland capability, but that’s up to the manufacturer.
Given how old the general aviation fleet in the U.S. is, you’re not going to see any planes with this feature at your local airport anytime soon, though. Most of those 1970s Cessna 150s for rent at your local FBO don’t even have an autopilot, after all.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2pwdnyF
via IFTTT

Comments
Post a Comment