How did Niantic happen? How did the company behind Pokémon GO and (soon) Harry Potter: Wizards Unite come to be?
When anyone talks about Niantic, they generally mention that it’s “a Google spinout” and move on. As if that’s something that just happens every day. That dozens of people within a massive company come together, build something… and then just leave and take their work with them to form a new, independent company that goes on to have a valuation of nearly 4 billion dollars.
So… how?
Over the last few weeks, I’ve interviewed dozens of people involved with Niantic’s story so far, including investors, executives, and employees past and present. I wanted to figure out the hows and whys of Niantic’s origins, what others might be able to learn from the company’s story so far, and where the company is going in the future.
The reading time for this article is 18 minutes (4,400 words)
The Keyhole into Google
“I started at Google with this idea that I’d be there for six months,” Niantic CEO John Hanke tells me.
We’re in a conference room at Niantic’s office, which takes up much of the second story of San Francisco’s Ferry Building. John’s wearing what I’ve come to realize is something of a daily signature for him: a T-shirt (often Niantic branded) beneath an unbuttoned blue dress shirt. His hair swoops forward and hangs just above his eyes. He’s laid back, but his words are very deliberate and still ring with the slightest hint of his Central Texas hometown.
“The whole time I was there,” he continues, “it felt like I’d be there for another six months. It just turned into 10 years.”
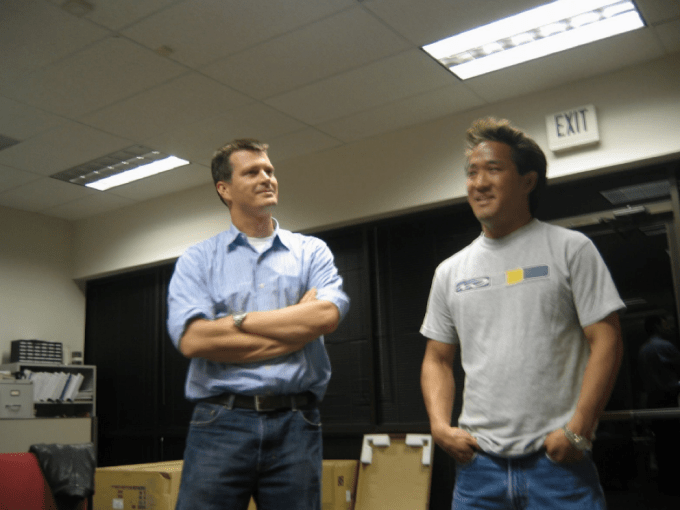

Keyhole’s John Hanke (left) and Chikai Ohazama (right) the day the Google acquisition closed in 2004. Photo by Brian McClendon
John started at Google in 2004 when it acquired his startup, Keyhole. Keyhole was a spin-out of sorts, too, growing its way out of a company called Intrinsic Graphics.
Intrinsic had set out to build a cross-platform video game engine – think Unity, but a decade and change too early. Along the way, the team at Intrinsic had built a demo that allowed users to zoom in and out of a wildly detailed view of the Earth. Like an interactive version of Powers of Ten, the user could parachute from a sprawling view of the entire globe all the way down to a bird’s eye view of their home with the flick of a mouse wheel. It was just a demo, but it was a very, very good one. Everyone seemed to care more about that demo than anything else Intrinsic was building.
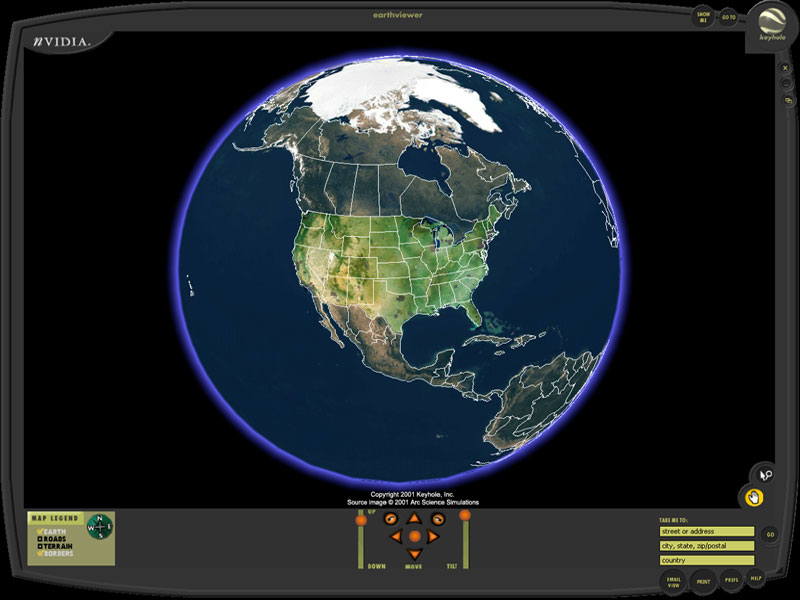
Keyhole’s Earth Viewer, circa 2002
Intrinsic hired John to build this demo into something more. When Intrinsic shut down operations in 2003, John and a handful of employees kept charging forward under the Keyhole name.
Keyhole never made a ton of money. A deal with CNN and an investment from In-Q-Tel (a venture capital firm backed by the CIA) kept it moving, but the ex-Keyhole folks I’ve talked to are pretty open about the company having danced on the edge of broke more than once before Google swooped in and bought it in 2004.
Keyhole’s earth viewer lives on to this day, of course. It’s just called Google Earth now.
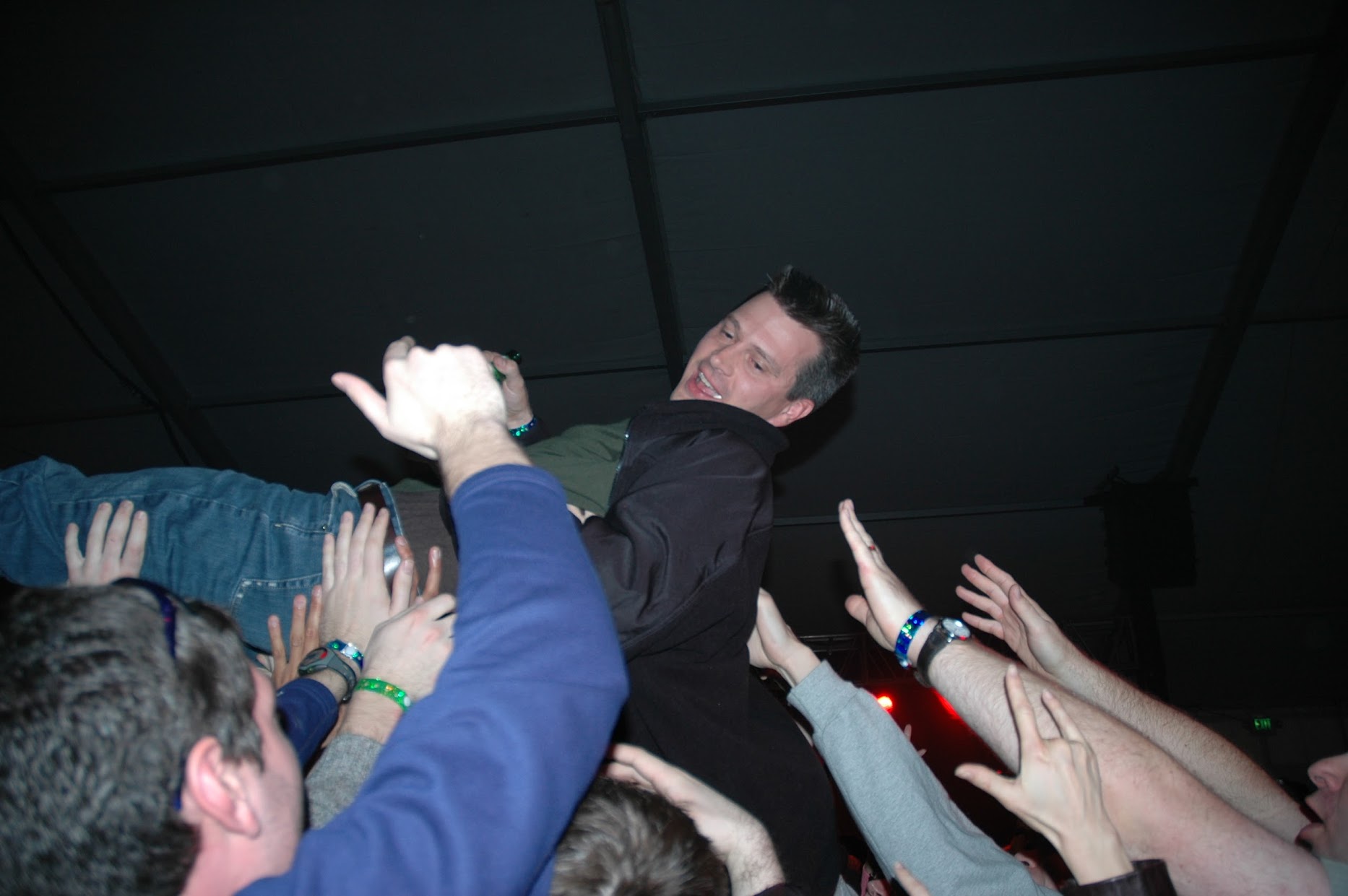

John Hanke being lifted up by his colleagues at a Google party a few months post-acquisition. Photo by the late Andria Ruben McCool, used with permission from her family.
Quitting Google to join … Google?
Flash forward to October of 2010, just a few months before the team that would become Niantic started to form. John’s intended “six months” at Google had just clicked over to its sixth year. He had spent that time leading Google’s Geo division — that’s Google Earth, Google Maps, and just about anything else that had to do with location. If you were typing a street address into something Google-branded, it was probably in a product John oversaw.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2Ovivv0
via IFTTT
Comments
Post a Comment