At the Adobe Summit in Las Vegas this week, privacy was on the minds of many people. It was no wonder with social media data abuse dominating the headlines, GDPR just around the corner, and Adobe announcing the concept of a centralized customer experience record.
With so many high profile breaches in recent years, putting your customer data in a central record-keeping system would seem to be a dangerous proposition, yet Adobe sees so many positives for marketers, it likely believes this to be a worthy trade-off.
Which is not to say that the company doesn’t see the risks. Executives speaking at the conference continually insisted that privacy is always part of the conversation at Adobe as they build tools — and they have built in security and privacy safeguards into the customer experience record.
Ben Kepes, an independent analyst says this kind of data collection does raise ethical questions about how to use it. “This new central repository of data about individuals is going to be incredibly attractive to Adobe’s customers. The company is doing what big brands and corporations ask for. But in these post-Cambridge Analytica days, I wonder how much of a moral obligation Adobe and the other vendors have to ensure their tools are used for good purposes,” Kepes asked.
Offering better experiences
It’s worth pointing out that the goal of this exercise isn’t simply to collect data for data’s sake. It’s to offer consumers a more customized and streamlined experience. How does that work? There was a demo in the keynote illustrating a woman’s experience with a hotel brand.
Brad Rencher, EVP and GM at Adobe Experience Cloud explains Adobe’s Cloud offerings. Photo: Jeff Bottari/Invision for Adobe/AP Images
The mythical woman started a reservation for a trip to New York City, got distracted in the middle and was later “reminded” to return to it via Facebook ad. She completed the reservation and was later issued a digital key to her room, allowing her to bypass the front desk check-in process. Further, there was a personal greeting on the television in her room with a custom message and suggestions for entertainment based on her known preferences.
As one journalist pointed out in the press event, this level of detail from the hotel is not something that would thrill him (beyond the electronic check-in). Yet there doesn’t seem to be a way to opt out of that data (unless you live in the EU and will be subject to GDPR rules).
Consumers may want more control
As it turns out, that reporter wasn’t alone. According to a survey conducted last year by The Economist Intelligence Unit in conjunction with ForgeRock, an identity management company, consumers are not just willing sheep that tech companies may think we are.
The survey was conducted last October with 1,629 consumers participating from eight countries including Australia, China, France, Germany, Japan, South Korea, the UK and the US. It’s worth noting that survey questions were asked in the context of Internet of Things data, but it seems that the results could be more broadly applied to any types of data collection activities by brands.
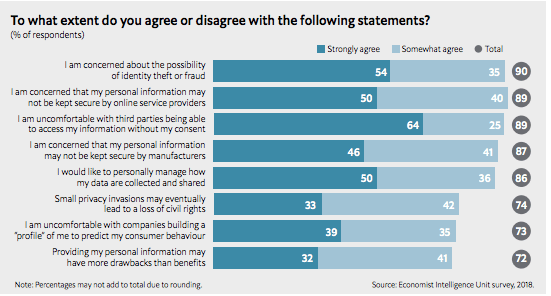
There are a couple of interesting data points that perhaps brands should heed as they collect customer data in the fashion outlined by Adobe. In particular as it relates to what Adobe and other marketing software companies are trying to do to build a central customer profile, when asked to rate the statement, “I am uncomfortable with companies building a “profile” of me to predict my consumer behaviour,” 39 percent strongly agreed with that statement. Another 35 percent somewhat agreed. That would suggest that consumers aren’t necessarily thrilled with this idea.
When presented with the statement, Providing my personal information may have more drawbacks than benefits, 32 percent strongly agreed and 41 percent somewhat agreed.
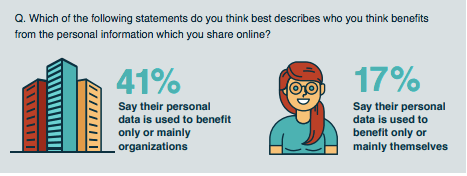
That would suggest that it is on the brand to make it clearer to consumers that they are collecting that data to provide a better overall experience, because it appears that consumers who answered this survey are not necessarily making that connection.
Perhaps it wasn’t a coincidence that at a press conference after the Day One keynote announcing the unified customer experience record, many questions from analysts and journalists focused on notions of privacy. If Adobe is helping companies gather and organize customer data, what role do they have in how their customers’ use that data, what role does the brand have and how much control should consumers have over their own data?
These are questions we seem to be answering on the fly. The technology is here now or very soon will be, and wherever the data comes from, whether the web, mobile devices or the Internet of Things, we need to get a grip on the privacy implications — and we need to do it quickly. If consumers want more control as this survey suggests, maybe it’s time for companies to give it to them.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2GmNGns
via IFTTT
Comments
Post a Comment